Papillomas are widespread in modern society. According to medical statistics, they are observed in one form or another in 80% of people and represent benign small tumors on the skin and mucous membranes of various parts of the body. They are just one of the manifestations of human papilloma virus (HPV) infection, whose strain is more than 190 species. There are viruses with high, medium and low oncogenic risk. Therefore, in addition to the aesthetic disadvantage, papillomas can pose a serious danger to human life and health, because some of them can transform into malignant tumors.
What is HPV
The human papilloma virus only infects humans, and its main route of transmission is sexual. Therefore, HPV is most common among sexually active individuals. This explains the fact that the infection most often occurs at a young age at the time of the onset of sexual activity and at its peak, ie 15-25 years. Moreover, several strains (types) of HPV can be present in the human body at the same time, causing the appearance of different types of tumor formations on the skin and mucous membranes.
The disease caused by HPV is called papillomatosis.
The virus infection occurs when it comes in contact with the skin or mucous membranes with particles of messy skin or mucous membranes of an infected person. They bind to the membranes of immature epithelial cells, from where they penetrate into the cytoplasm of the cell, and then into the nucleus. DNA is contained in the cell nucleus, which is damaged by HPV. As a result, when an affected cell divides, the result will be the creation of new healthy cells, but which already have altered genetic information, leading to disturbances in the mechanism of their reproduction and differentiation. This becomes the reason for the appearance of tumors on the skin and mucous membranes.
HPV infection can lead not only to the formation of papillomas, but also to warts, as well as flat and genital warts. However, it can be asymptomatic. In this case, the patient will not show external signs of human papilloma virus infection, but will act as a carrier and may infect others during unprotected intercourse or at home.
Thus, HPV infection does not always lead to the formation of papillomas. It depends on the strength of the person's immunity, but more often the first small papillomas appear 1-6 months after the infection.
The human papilloma virus is intracellular. Therefore, with sufficient strength of the immune system, the body successfully suppresses its activity and does not provide an opportunity to cause cell proliferation. But with the weakening of immunity as a result of the action of certain factors, the body's defenses fall, the virus is activated, leading to the formation of papillomas.
All strains or types of HPV can be divided into 4 groups:
- neoncogenous - strains 1-5, 63;
- low oncogenic risk - strains 6, 11, 40, 42-44, 54, 61, 70, 72, 81;
- medium oncogenic risk - strains 26, 31, 33, 35, 51-53, 58, 66;
- high oncogenic risk - strains 16, 18, 39, 45, 56, 59, 68, 73, 82 (types 16 and 18 are considered the most dangerous).
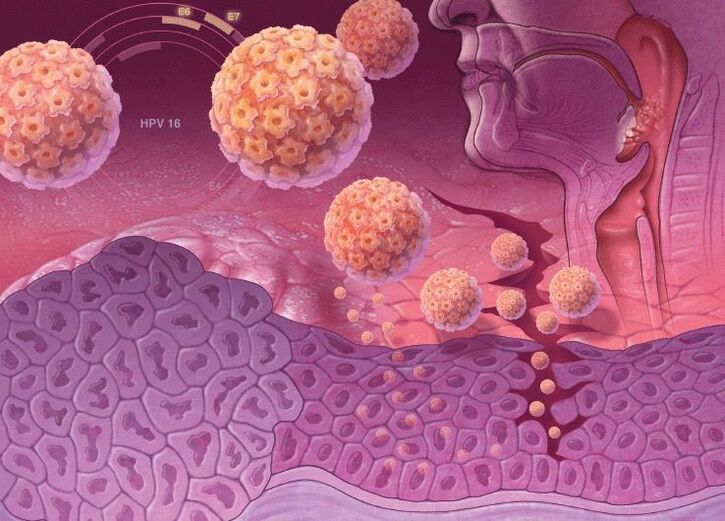
HPV strains of high oncogenic risk have special genes in their DNA that are responsible for the synthesis of specific proteins, oncoproteins (E6 and E7). Therefore, when it is incorporated into the DNA of a human cell, its protection against cancer is reduced. Oncoproteins destabilize the genome of a skin cell, provoke its active reproduction and suppress the ability to differentiate. Therefore, this is fraught with a high risk of developing cancer when infected with human papillomavirus strains of high oncogenic risk.
The magnitude of the danger posed by papillomas directly depends on the type of HPV. Infection with strains with a high oncogenic risk is dangerous for the development of:
- cervical cancer;
- malignant tumors of the anus, vulva, penis;
- oropharyngeal carcinoma, etc.
70% of cervical cancers are due to HPV types 16 and 18.
But even when they are infected with low-oncogenic risk strains and the formation of papillomas, they should be treated with care. Convex neoplasms are often injured by clothing, bleed, and often become inflamed. At the same time, perhaps the greatest discomfort comes from the formations on the genitals, which cause severe discomfort and make it difficult to lead an intimate life. In such cases, it is possible to attach a secondary infection that can cause the development of purulent-septic complications. In addition, papillomas can form on the mucous membranes of almost all internal organs, leading to disturbances in their work. Thus, papillomatosis of the upper respiratory tract is often found, which causes difficulty in breathing.
Causes of papillomas and risk factors
HPV can be transmitted sexually, as well as from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth. The route of transmission of the virus by contact with the household, ie by sharing towels, clothes, etc. , is not excluded. This explains the high prevalence of HPV in the world. Self-infection is also possible. In this case, if one papilloma is injured, the virus can be transmitted to healthy areas of the skin and affect them.
The main causes of HPV infection are frequent changes of sexual partner and unprotected sexual intercourse.

But infection with the virus does not always lead to the formation of papillomas, genital warts, etc. The probability of developing papillomatosis depends on various factors:
- immunodeficiency of any origin, including taking drugs that suppress immunity (immunosuppressants, cytostatics, etc. ), the presence of HIV infection, radiation damage;
- reduction of the body's defenses against the background of physiological changes during pregnancy;
- early onset of sexual activity, when the immune system is not yet fully formed and strengthened;
- microtrauma of the skin and mucous membranes;
- infection with highly oncogenic strains of HPV;
- the presence in the body of several types of HPV at the same time;
- the presence of other sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), especially gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, herpes, cytomegalovirus infection, Epstein-Barr virus, hepatitis B and C, etc. ;
- hormonal disorders;
- exhaustion, hypovitaminosis, chronic fatigue and severe stress;
- more births and abortions;
- the presence of severe chronic diseases, especially diabetes mellitus;
- leading an unhealthy lifestyle, the presence of bad habits;
- poor living conditions.
Elderly and overweight people are more prone to developing papillomas. Moreover, their neoplasms often form in the folds of the skin, which contributes to their injuries and inflammation.
Types and symptoms
Neoplasms caused by HPV infection can form on the skin and mucous membranes of various parts of the body, including the face, neck and décolleté. They can also form on the arms, legs, back, genitals, including the perineum, labia majora and major, vulva, vagina, cervix, penis, especially along the coronary groove and frenulum. Damage to the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, tongue, nasopharynx, esophagus, bladder, conjunctiva, trachea and other internal organs is not excluded.
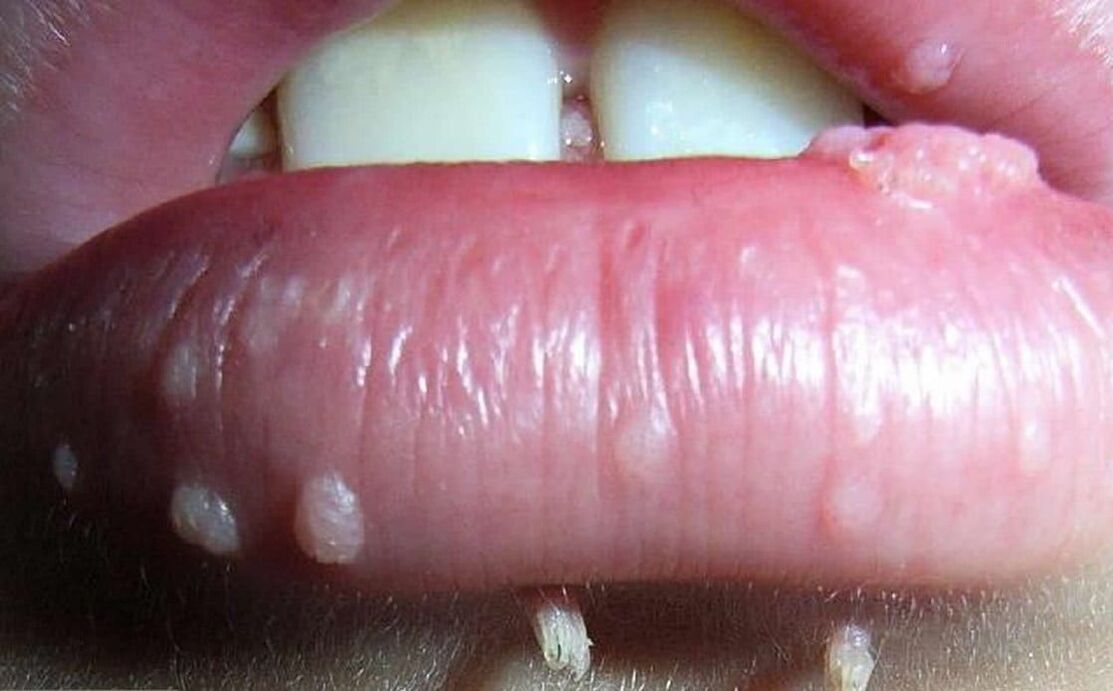
Human papilloma virus can lead to the appearance of tumors of various natures. They can generally be divided into 3 groups, although in all cases the reason for their appearance is the same - human papilloma virus infection.
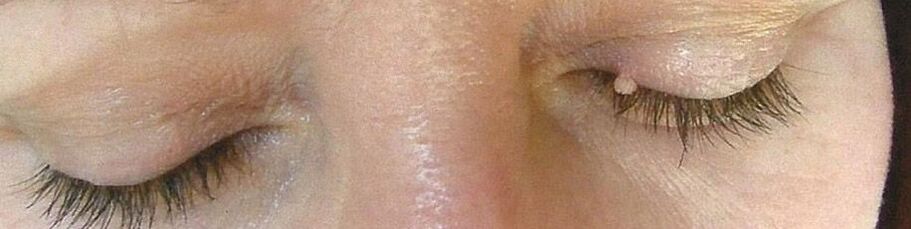
- Papillomas are benign neoplasms of pink, white, pearl or light brown color, which most often occur on the eyelids, lips, chest, armpits, neck. They are located on their own and usually do not tend to merge, even with multiple lesions. Papillomas are usually round or lumpy, resembling a cauliflower head, more often having a leg.
- Warts are benign formations of dirty brown or pale color in the form of a rooster or a set of fringes united by a common base. They are most commonly found in the genital area, anus and around the mouth. They tend to merge with each other and as a result cover large areas of the body. Their appearance is due to HPV infection types 6 and 11. Distinguish between pointed, straight and intraepithelial warts.
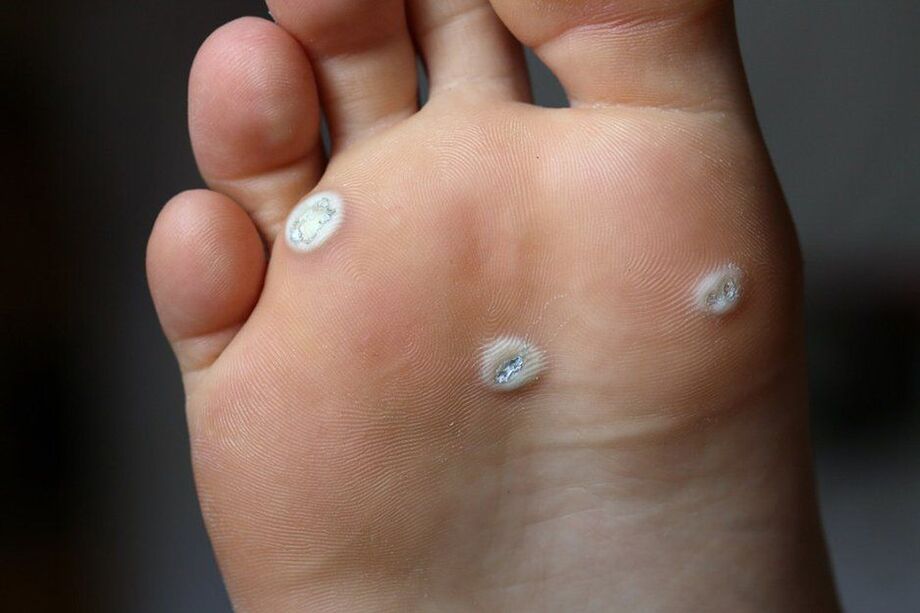
- Warts are uneven, light, benign tumor formations in the form of plaque or small nodules on the surface of the skin of the hands, on the nails, feet, face and front of the body. Warts may look like papillomas, but they differ in a wide base. They usually occur in HPV infections of types 1-5, 7-10, 12, 14, 15, 17, 19-24.
Such tumor-like formations can vary in size from a few millimeters to large growths that cover large areas of skin or mucous membranes.
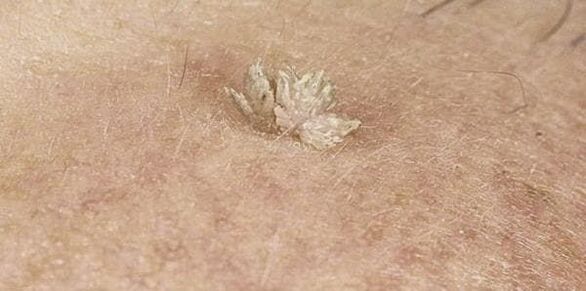
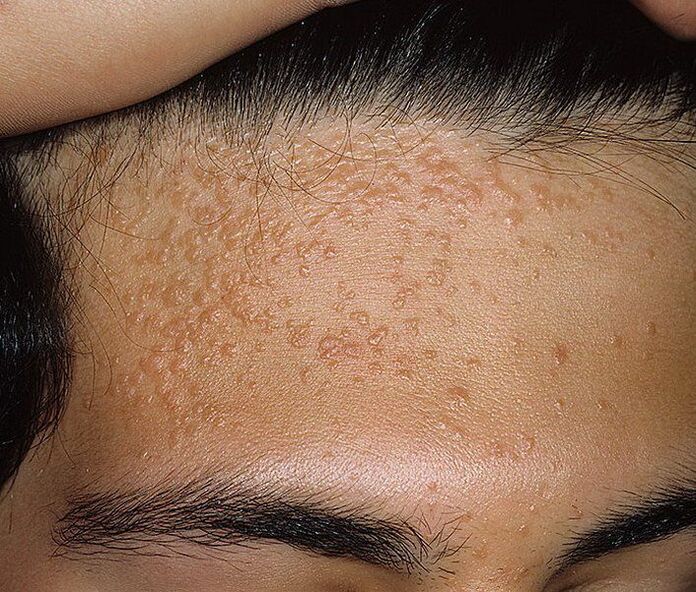
Also, neoplasms can vary in appearance, which directly depends on the type of HPV that has entered the body. More often than others there are:
- Vulgar or ordinary - bulges of dense consistency with a diameter greater than 1 mm. They tend to merge and group together.
- Plantar warts are raised above the surface of the skin, often painful bumps with a shiny surface and rim. A characteristic feature is the absence of a skin sample. Their formation is caused by HPV types 1, 2, 4.
- Flat papillomas are soft, smooth, flat, usually rounded growths that have a normal skin color or slightly yellowish, pink. They can cause itching, so they are often injured, painful and inflamed. The cause is HPV strains 3 and 10.
- Filiforms (accordes) are one of the most common papillomas, especially among elderly patients. They are most often found on the face, around the eyes, in the groin, armpits, and neck. They are yellowish in color and have a tendency to grow gradually, turning into nodules of thick but elastic consistency.
- Genital warts in the perineum, genitals.
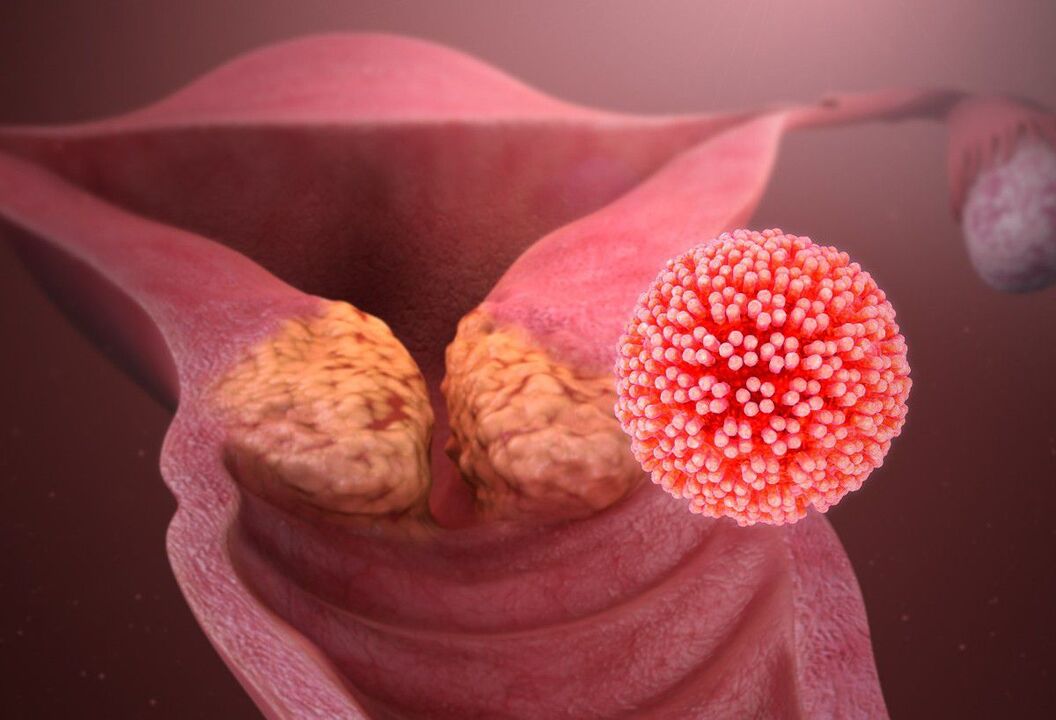
Papillomas may be visible to the naked eye or located in the thickness of the skin or mucosa. In the latter case, they are called endophytes, and one of their manifestations is cervical dysplasia. Defeat of papillomatosis of female internal genital organs may indicate:
- itching, stinging, crying in the perineum;
- abundant leukorrhea;
- bloody discharge, especially after sexual intercourse;
- discomfort during intimacy.
Sometimes papillomatosis can cause back and pelvic pain, weakness, swelling of the legs and unnecessary weight loss. Such signs are among the most alarming, because they can indicate the development of complications of HPV infection.
Diagnosis
If papillomas form on the body, face or genitals, you should consult a dermatologist. This will enable not only the diagnosis of human papilloma virus infection in the early stages, but also the taking of measures to prevent the creation of new elements, as well as the observation of changes in the existing ones.
It is especially important not to hesitate to visit a doctor if there are signs of growth, discoloration of the papilloma, unpleasant odor or pain in the area of its localization.
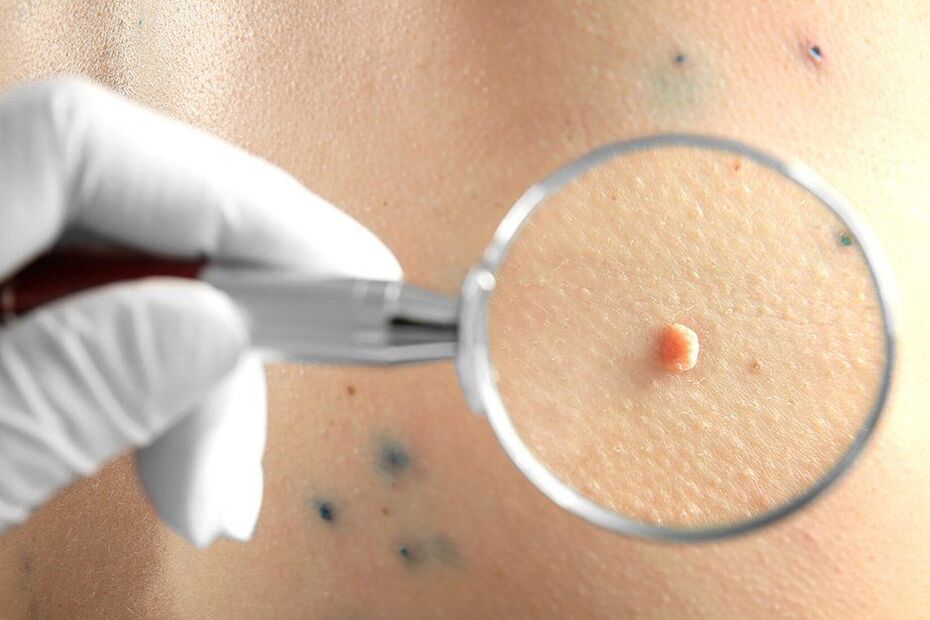
First of all, the doctor will perform a dermatoscopy, ie examination of the tumor using a special magnifying device. This will enable the determination of their nature, as well as the observation of dangerous signs that indicate a high probability of degeneration of the benign formation into malignant, not to mention the formed cancer. If detected at an early stage of development, they can be successfully treated and have a favorable prognosis in the future.
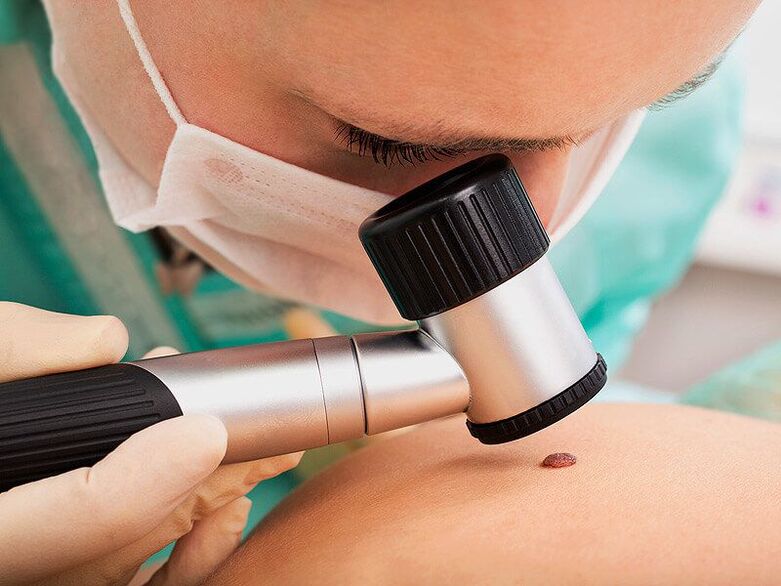
It is necessary to recommend that patients be tested for sexually transmitted diseases, especially if warts are found in the genital area. Also, in such situations, it is shown that women receive advice from a gynecologist and men from a urologist. This is important to diagnose the presence of a cervical lesion, urethra, human papilloma virus, and, if necessary, prescribe appropriate treatment.
To confirm papillomatous infection, patients are usually assigned a PCR analysis. With its help, it is possible not only to confirm or deny the infection with the human papilloma virus, but also to precisely determine the strains.
Treatment and removal of papillomas
The treatment of human papilloma virus infection is always complex. Of course, disturbing papillomas can be easily removed, but in this case there is a great risk that a new one or even several will soon be created in its place. Because the main reason for the formation of papillomas is a decrease in their own defenses, which allows dormant HPV to become active, first of all, patients with papillomatosis are prescribed drug therapy. It involves taking immunomodulators and antiviral drugs. In addition to extensive skin and mucosal lesions with papillomas, cytotoxic drugs may also be prescribed. But they are taken under the supervision of a doctor because they can cause serious side effects.
If a patient is diagnosed with concomitant infections or illnesses, appropriate treatment for the situation must be prescribed, and sometimes additional consultation with a specialist and undergoing therapy under his supervision is required.

Warts of all kinds are subject to mandatory removal, as are papillomas, which are often injured and inflamed. In other cases, removal is done at the request of the patient. But it is possible to begin to remove the visible manifestations of HPV infection only after the completion of treatment of concomitant diseases, if any, and in the background of the continuation of antiviral therapy.
In general, all modern methods of destruction or removal of papillomas can be divided into 2 major groups:
- chemical - consists of the use of various chemical compounds to remove papillomas, including trichloroacetic acid, dermatological preparations;
- physical - involves the removal of papillomas by surgery, electrocoagulation, cryodestruction, laser, coagulation of radio waves or plasma.
After removing a papilloma by one method or another, it is important to use local remedies prescribed by your doctor to speed healing and eliminate the risk of infection.
The success of treatment, and especially the removal of papillomas, depends on the strength of the immune system. In its normal state, in 90% of cases, within 2 years from the moment of infection, HPV is suppressed or even completely destroyed. But that is not a guarantee that there is no risk of re-infection or the formation of new papillomas. If the immunity is reduced by the action of certain factors, papillomatosis becomes chronic, occasionally recurs and can lead to serious complications.
To prevent infection with dangerous strains of HPV and the development of severe complications, it is recommended, especially for girls, to be vaccinated between 9 and 25 years of age.
Surgical removal of papillomas
The essence of the method is the removal of the neoplasm with a scalpel, which is associated with the formation of scars and increased healing time. Therefore, it is used only when it is necessary to remove a large papilloma or in those cases when it is necessary to perform a histological examination, since the formation of malignant cells in it is assumed.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, which makes it painless. The doctor uses a scalpel to remove the tumor itself and grasps the surrounding healthy tissue. This is necessary to eliminate the risk of recurrence of the papilloma in the same place. If he has a leg, he dissects it with surgical scissors, and with the help of an electrocoagulator, the blood vessel that fed the neoplasm is "sealed". The remaining wound is sutured, treated with antiseptic and covered with a sterile bandage.
Today, surgical removal of papillomas is usually performed when there is a suspicion of the formation of cancer cells.
Cryodestruction
The method involves the use of low temperatures to destroy papilloma cells. This is achieved by using liquid nitrogen whose temperature is -196 ° C. The essence of the procedure is the use of a special nozzle or touching the papilloma with a cotton cloth dipped in liquid nitrogen. Under its action, the water contained in the cells instantly turns into ice crystals that destroy them from within. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia or without it, because the exposure time to liquid nitrogen does not exceed 5-20 seconds.
The complexity of the method lies in choosing the exact duration of exposure so that the papilloma is removed at full depth and does not harm healthy tissues, which will lead to the formation of scars.
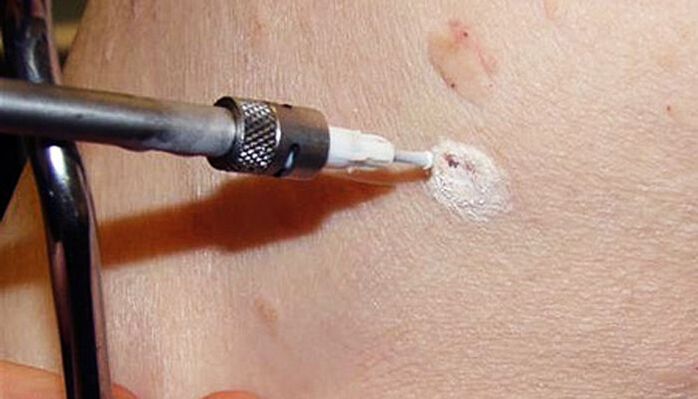
Immediately after treatment with liquid nitrogen, a white spot forms at the site of the papilloma. After that, a small bubble with a transparent or pink liquid content forms on it, and the surrounding skin turns red and may swell a little. This may be accompanied by minor discomfort in the form of a burning or tingling sensation.
After 3-4 days, the bladder bursts, and in its place a crust is formed which itself disappears after a few days, revealing healthy young skin. Under no circumstances should you puncture, injure or otherwise injure the bladder on your own.
Cauterization of papilloma with liquid nitrogen is possible only in cases when the possibility of malignant cells in it is completely excluded. This method is most commonly used to remove papillomas and genital warts at:
- century;
- face;
- small joints;
- genitals.
Laser papilloma removal
The use of lasers to remove papillomas is also possible only in cases where their malignancy is completely ruled out. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, and consists of evaporating moisture in the papilloma cells with the thermal energy of a laser. Thus, the focused laser beam is directed at the neoplasm. The duration of the presentation does not exceed 1 minute.
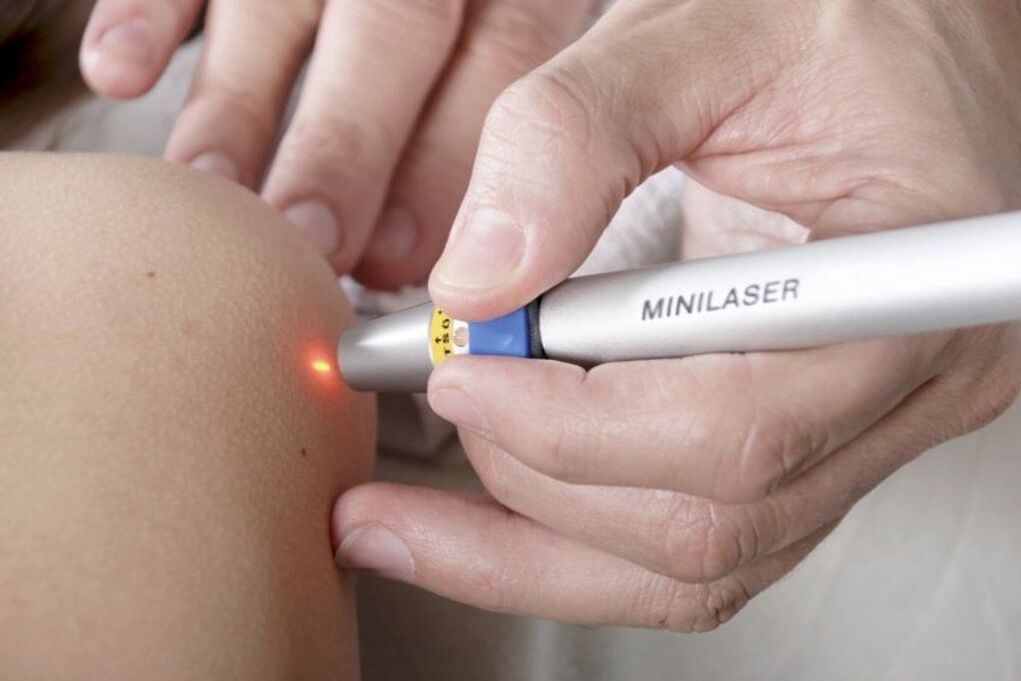
As a result, a crust forms at the site of the papilloma, and the skin around it becomes red and swollen. The bark will disappear on its own within a week. It cannot be soaked and steamed for 3 days, nor can it be torn off and injured, because it is filled with scars. In addition, within 2 weeks after papilloma removal it is worth protecting the treatment area from sunlight. Otherwise, there is a high probability of hyperpigmentation of this area.
When removing papillomas on the face with a laser, do not apply decorated cosmetics to the affected area until complete healing.
After the peeling off, a healthy pink skin is revealed, which gradually takes on a normal shade. This is the main advantage of laser papilloma removal, because it does not involve the formation of scars and scars. They can be created only when large neoplasms are removed and the rules of care in the postoperative period are violated. Also, laser removal completely eliminates the risk of wound infection and is an absolutely bloodless method, because under the influence of thermal energy, there is an immediate coagulation of small blood vessels.
With the help of laser papillomas are mainly removed on:
- hands;
- legs and feet;
- face;
- century;
- neck;
- genitals.
Laser is the only reliable way to remove plantar warts, because their roots can enter 1 cm or more into the tissue.
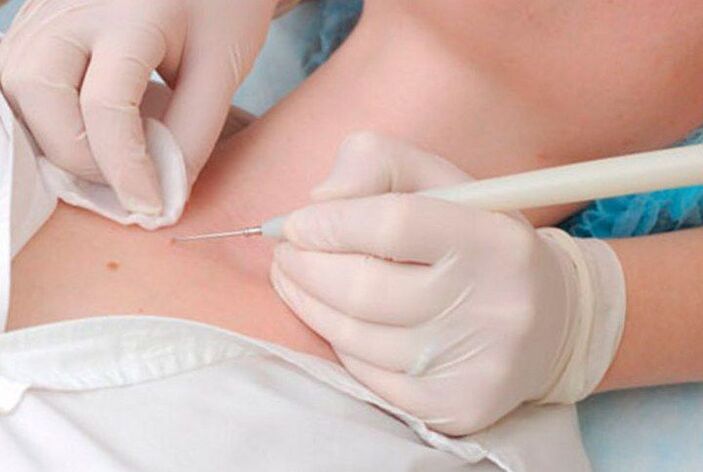
Electrocoagulation of papillomas
The essence of the method is to use electric current to remove papillomas. Using a special device called an electrocoagulator, the doctor grasps the papilla and cuts it inside the healthy tissue. In this case, there is no bleeding at all, because the thermal energy of the current is sufficient for the coagulation of small blood vessels. But the procedure can be painful, especially if it is necessary to remove growths on parts of the body with delicate skin.
After electrocoagulation, a crust is formed. And the whole recovery period lasts 7-10 days. After the bark falls off, the skin under it should be protected from damage and exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
The method is used to remove papillomas in different parts of the body. Moreover, electrocoagulation can also be used in cases when it is necessary to perform a histological examination of the neoplasm and precisely determine its nature. But the outcome of the procedure depends entirely on the qualifications and experience of the doctor, however, as in other cases, because if the removal is not deep enough, the papilloma can re-form in the same area.
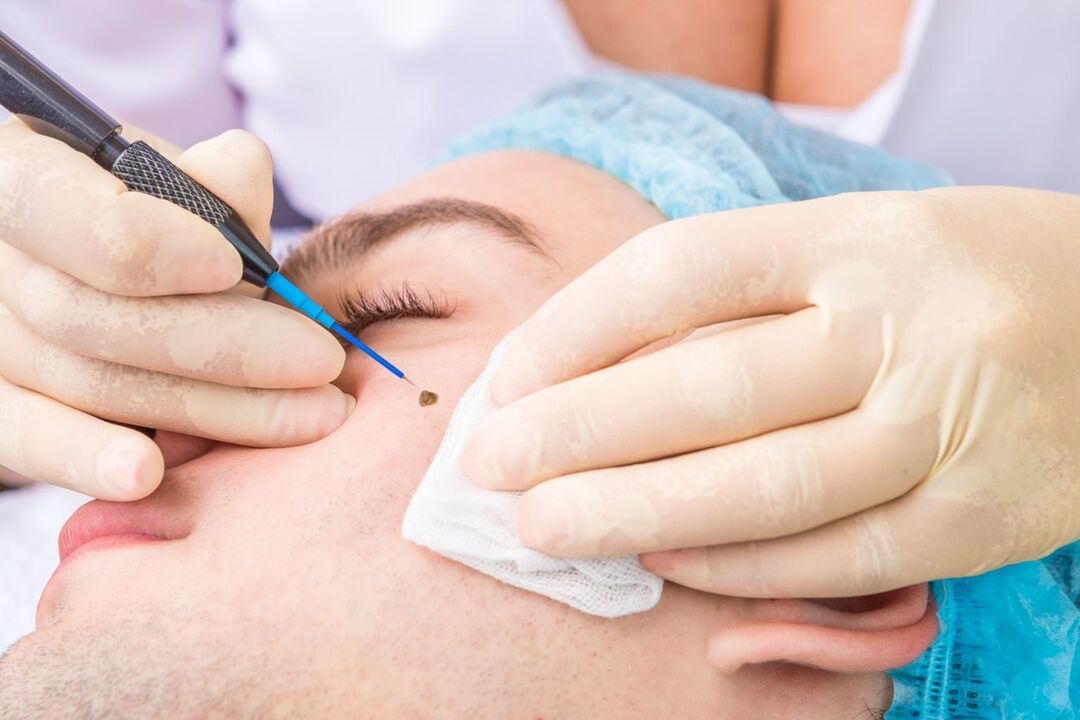
Radiowave surgery
This method is one of the most advanced in removing papillomas of any kind. It involves the use of special devices. But at the same time it has a lot in common with laser papilloma removal. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, and removal occurs directly due to exposure of the neoplasm to radio waves. Thanks to them, it is possible to completely cut off papillomas of any size and location, as well as avoid scars.
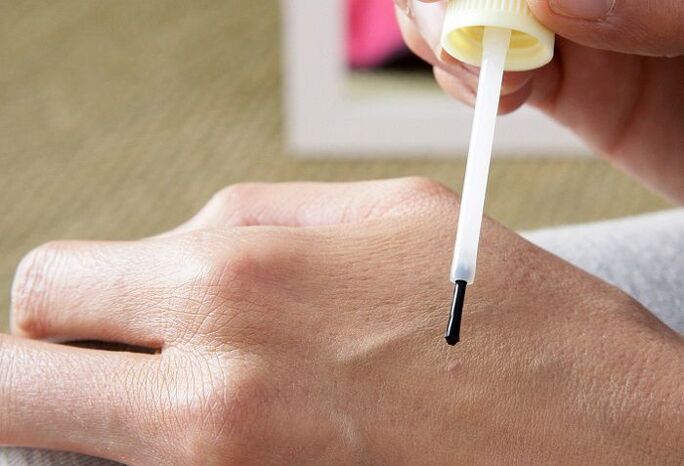
Chemical removal of papillomas
The method includes regular application of special compounds on papillomas, which destroy their cells, which leads to the disappearance of the tumor. But when using such drugs, it is important to be extremely careful and not allow the substance to come into contact with healthy skin.
So, everyone can face the formation of papillomas. There is no effective prevention of HPV infection, and vaccines only protect against the most dangerous strains of the virus in terms of cancer risk. However, in most cases, they do not create significant discomfort to the person, except for the genital warts and anus, which must be removed. In any case, you can get rid of any papillomas quickly and efficiently, but since it is impossible to completely destroy HPV in the body with medication, and there is always a risk of re-infection or another strain, there is a possibility that the problem will return. The only reliable way to reduce the likelihood of papilloma is to strengthen the immune system. And if they appear and represent a cosmetic defect or interfere with a person's daily life, consult a dermatologist. The doctor will be able to accurately distinguish papillomas from other skin neoplasms and will solve this problem in a matter of minutes.























